Time:2025-11-04 06:15:59 Source:Sanjian Meichen Steel Structure
Steel structures play a fundamental role in industries that rely on heavy machinery. These structures are meticulously designed to support the enormous weight, vibration, and stress exerted by large-scale industrial equipment. Whether you're operating cranes, turbines, industrial presses, or any other large machines, a well-designed steel structure ensures the equipment performs efficiently, safely, and reliably. This article provides an in-depth look at how steel structures support heavy machinery, the critical design elements involved, and the considerations needed for successful installation and maintenance.
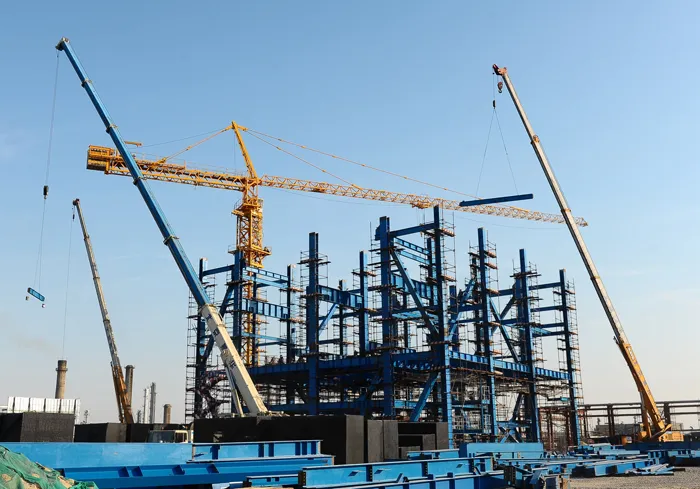

Heavy machinery can weigh several tons and often requires specialized support to ensure safe operation and efficient performance. Steel structures are the material of choice for these applications due to their exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. They can withstand enormous loads, dynamic forces, and vibrations without compromising stability. Steel structures are crucial for the following reasons:
Machine Foundations: The foundation is perhaps the most critical element in supporting heavy machinery. Steel structures help create solid, stable bases that can distribute the weight of machinery like industrial presses, cranes, or turbines, which often exert forces far beyond typical construction loads.
Support Frames: These frames act as the primary load-bearing elements for machinery. They ensure that equipment remains stable and correctly aligned during operation. Examples include steel frames for conveyor systems, large generators, and manufacturing lines.
Platforms and Walkways: Steel structures are used to create platforms and walkways that offer safe access for operators and maintenance teams. These structures need to be sturdy enough to handle the load from both personnel and machinery.
When designing steel structures for heavy machinery, there are several key considerations to ensure that the structure is safe, reliable, and capable of withstanding the forces exerted by large industrial equipment. Below are the primary factors to focus on during the design phase:
Heavy machinery generates substantial forces that must be evenly distributed across the steel structure. These forces can include static loads (the weight of the machinery itself) as well as dynamic loads (forces produced by operation, such as vibration, shock, and torque). To ensure stability and safety, the steel structure must be designed to:
Distribute Loads Evenly: The weight and forces exerted by the equipment need to be distributed across the structure to avoid localized stress that could lead to structural failure.
Accommodate Dynamic Forces: Machinery like presses and turbines can generate high levels of vibration and impact. The steel structure must be designed to absorb and dampen these forces to prevent structural fatigue or failure.
Steel structures used to support heavy machinery are often exposed to harsh environments, including moisture, high temperatures, chemicals, and corrosive elements. As such, corrosion resistance is critical to the longevity of the steel structure.
Coatings and Finishes: Applying protective coatings such as galvanized steel or epoxy coatings can help prevent rust and corrosion. These coatings ensure the structure remains intact despite exposure to environmental stressors.
Environmental Considerations: In environments where steel is exposed to extreme humidity or chemicals (e.g., coastal areas or manufacturing plants), the selection of corrosion-resistant steel grades and coatings is essential.
Many types of heavy machinery produce significant vibrations and shocks during operation. These forces can cause structural degradation over time, leading to potential failures or inefficiencies. Steel is inherently capable of absorbing vibrations, but it’s essential to design the structure to minimize these impacts.
Vibration Dampening Systems: Integrating vibration dampeners, such as rubber pads or spring mounts, can reduce the effect of vibrations. These systems prevent excessive movement of both the machinery and the steel structure.
Shock Absorption: Steel beams and joints that can absorb shocks are crucial, especially when dealing with high-impact machinery like industrial hammers or presses. Shock-absorbing elements prevent the equipment from transferring damaging forces to the structure.
The manufacturing of steel structures for heavy machinery involves multiple steps to ensure the structure is robust and capable of handling the stresses imposed by large equipment. This includes precise engineering, fabrication, quality control, and transportation.
The process begins with a detailed design phase. Structural engineers must calculate the exact load-bearing capacity required for the steel structure, taking into account the machinery's weight and the forces it will exert during operation.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Tools like Tekla Structures or AutoCAD are used to model the structure in 3D, ensuring that all components are accurately dimensioned and that the assembly process will be seamless.
Once the design is approved, the steel components are fabricated in a controlled factory setting. This involves cutting, welding, and assembling the steel into the components needed for the structure. During fabrication, quality checks are conducted to ensure that each part meets design specifications and tolerances.
Welding Inspections: All welds must be thoroughly inspected to ensure they are structurally sound and free of defects.
Dimensional Accuracy: The fabrication process ensures that all steel parts are within precise tolerances, so they fit together perfectly when assembled on-site.
After fabrication, the steel components are transported to the installation site. Given the large size and complexity of the structure, careful logistical planning is needed to ensure safe and timely delivery.
Site Preparation: The foundation must be prepared to accept the steel structure, and the surrounding area must be cleared and leveled. This may involve excavation, soil stabilization, and concrete pouring.
Assembly On-Site: The steel components are assembled on-site using cranes and other heavy lifting equipment. It’s essential that assembly follows the pre-planned design to ensure the structure's integrity and safety.
The installation of steel structures is a critical phase of the project, as it ensures that the machinery is securely supported and positioned. The process typically involves:
A strong and stable foundation is essential for supporting both the steel structure and the heavy machinery. Poorly designed foundations can lead to settlement or shifting over time, jeopardizing the machinery's operation.
Soil Analysis: A thorough analysis of the soil conditions is needed to determine the type of foundation (e.g., deep foundations, slab-on-grade) and ensure it can bear the load of the equipment.
Reinforced Concrete: Most heavy machinery installations require reinforced concrete foundations that are capable of distributing the machinery's weight evenly.
The steel frame supporting the machinery must be assembled according to precise specifications. The support frame must be aligned correctly to ensure the machinery operates at its full capacity without issues.
Securing Components: All connections and fastenings must be secured, including bolts, welds, and anchors, to prevent any movement or misalignment.
Once the steel structure is in place, the heavy machinery is installed. This step involves positioning the equipment correctly, securing it to the structure, and connecting necessary power, mechanical, and hydraulic systems.
Final Adjustments: The machinery is calibrated, ensuring all components function efficiently and that the installation meets operational specifications.
Ongoing maintenance is essential to ensure the steel structures supporting heavy machinery remain operational for decades. Preventive maintenance can extend the life of both the structure and the equipment.
Routine inspections help detect early signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. These inspections should include checking for structural cracks, rust, and any signs of shifting or misalignment.
Preventive measures like lubricating joints, cleaning, and repainting steel parts will ensure the structure's longevity and performance. Keeping up with regular maintenance helps prevent costly repairs down the line.
Steel structures are essential for the safe and efficient operation of heavy machinery in industries ranging from manufacturing and construction to energy production and logistics. With their ability to bear heavy loads, resist dynamic forces, and provide long-term durability, steel structures ensure that large-scale equipment functions at full capacity. By understanding the critical design, fabrication, installation, and maintenance considerations, companies can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of their steel structures supporting heavy machinery.