1. Introduction
In today’s fast-paced industrial and commercial sectors, steel structure warehouses have become the cornerstone of efficient storage and logistics management. From e-commerce fulfillment centers and cold chain facilities to large-scale manufacturing plants, these warehouses support global supply chains with strength, speed, and scalability.
A steel structure warehouse is primarily built using prefabricated steel components — such as beams, columns, trusses, and wall cladding systems — that are engineered and manufactured in a factory before being assembled on-site. This prefabrication method ensures precision, consistency, and faster construction timelines, which are critical for modern businesses seeking rapid setup and operational efficiency.
The demand for steel structure warehouses continues to grow, driven by:
-
The expansion of global logistics and e-commerce.
-
The rise of automated warehousing systems that require large, column-free spaces.
-
The need for durable, low-maintenance buildings that can withstand harsh industrial environments.
Unlike conventional concrete or masonry warehouses, steel structure warehouses provide lightweight yet high-strength frameworks, offering unmatched flexibility and cost savings across the building’s lifecycle. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know—from design and construction principles to selection criteria and maintenance best practices.
2. Basic Concept of Steel Structures
What Is a Steel Structure?
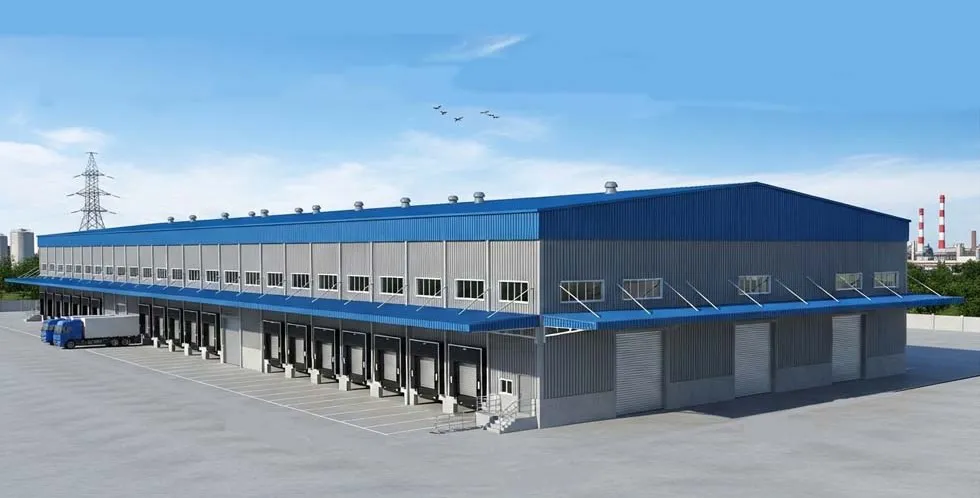

A steel structure refers to a load-bearing framework made primarily of structural steel components such as H-beams, box columns, and lattice trusses. Thanks to steel’s high tensile and compressive strength, these structures can achieve larger spans, greater heights, and higher load capacities than buildings made from reinforced concrete or wood.
Steel structures are typically composed of:
-
Primary framing (columns and beams) that form the skeleton of the building.
-
Secondary framing (purlins, girts, and bracings) that support roofing and walls.
-
Enclosure systems (roof panels, wall cladding, insulation) that complete the building envelope.
Because steel components are prefabricated in factories with CNC cutting, automatic welding, and Tekla 3D modeling systems, the on-site assembly process is faster, cleaner, and more predictable—reducing labor intensity and construction risk.
Advantages of Steel Structures
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:
Steel provides exceptional load-bearing performance with minimal material usage, ideal for long-span warehouses or mezzanine systems.
Lightweight and Economical Foundations:
Steel’s low self-weight reduces foundation loads and overall construction costs, especially on weak soil conditions.
Modular and Prefabricated:
Components can be mass-produced, transported, and bolted together quickly on-site, significantly reducing project duration.
Adaptability:
Steel warehouses can be easily expanded, relocated, or modified, making them perfect for businesses expecting future growth or process changes.
Why Steel Structures Dominate Modern Industrial Architecture
The global shift toward smart manufacturing, logistics automation, and sustainability has made steel structures indispensable. They offer:
-
Flexible layouts for automated conveyor systems and forklift traffic.
-
Energy-efficient envelope designs that integrate solar panels or natural lighting.
-
Compliance with international green standards such as LEED and ISO 14001.
Steel Structure Warehouse vs. Traditional Concrete Buildings
|
Feature
|
Steel Structure Warehouse
|
Concrete/Brick Warehouse
|
|
Construction Speed
|
30–50% faster (prefabricated assembly)
|
Slow (curing, weather delays)
|
|
Cost Efficiency
|
Lower lifecycle cost
|
Higher labor and maintenance cost
|
|
Span Flexibility
|
Up to 80–100m clear span
|
Limited by column spacing
|
|
Environmental Impact
|
Recyclable, lower CO₂ footprint
|
High energy consumption in cement
|
|
Maintenance
|
Minimal, with anti-corrosion coatings
|
Frequent repairs and painting
|

3. Key Benefits of Steel Structure Warehouses
1. Space Efficiency and High Utilization
Steel structure warehouses provide large column-free interiors, maximizing usable floor space. This is essential for:
-
High-rack storage systems
-
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
-
Production lines requiring wide, unobstructed zones
With roof trusses and portal frames optimized through structural analysis, these warehouses achieve clear spans exceeding 100 meters, ideal for logistics and distribution centers.
2. Fast Construction and Short Lead Time
Steel components are fabricated concurrently with foundation work, drastically shortening total project schedules. Compared with concrete buildings, steel warehouses can be completed 20–40% faster, helping investors begin operations and generate ROI earlier.
3. Long-Term Durability
Steel structures are engineered to perform for decades under demanding industrial conditions:
-
Hot-dip galvanizing and epoxy coatings prevent corrosion.
-
Wind and seismic-resistant design ensures stability in adverse climates.
-
Fireproof paint systems enhance building safety and compliance with international codes.
4. Cost and Energy Efficiency
While initial investment may be comparable, steel structures offer significant savings through:
-
Lower maintenance costs
-
Reduced energy consumption with insulated wall panels
-
Shorter project cycles leading to earlier revenue generation
4. Components of a Steel Structure Warehouse
|
Component
|
Description
|
Function
|
|
Steel Columns
|
H-section or box columns
|
Vertical load transfer
|
|
Steel Beams
|
Main and secondary beams
|
Roof/floor support
|
|
Bracings
|
Cross or K-type
|
Wind and seismic stability
|
|
Roof Purlins
|
C/Z sections
|
Roof panel support
|
|
Wall Girts
|
C/Z sections
|
Wall cladding support
|
|
Roof Panels
|
Color-coated or sandwich panels
|
Weather protection
|
|
Wall Panels
|
Sandwich panels or corrugated sheets
|
Thermal and sound insulation
|

Construction Process Overview
1. Design Phase:
Engineers use 3D modeling software (e.g., Tekla Structures, STAAD.Pro) for precise load simulation and detailing.
2. Fabrication:
Steel plates and sections are cut, welded, drilled, and surface-treated in controlled factory environments.
3. Transportation:
Prefabricated members are delivered in sequence for efficient on-site erection.
4. Assembly:
Using cranes, steel frames are bolted and welded into position, followed by roof/wall installation.
5. Inspection & Handover:
Final quality checks ensure compliance with ISO, ASTM, or EN standards.
5. Design of Steel Structure Warehouses
Design Principles
Designing a steel structure warehouse involves considering various factors:
-
Load Requirements: This refers to the weight the warehouse must support, including equipment, goods, and shelving. The design must ensure the structure can safely bear these loads without risk of failure.
-
Space Layout: Proper space planning is critical. The warehouse needs to accommodate specific functions such as storage, production, and shipping, with efficient pathways for forklifts and personnel.
-
Building Codes: Local building codes dictate safety standards, fire protection, and structural requirements that the warehouse must comply with.
Space Planning
The design can be tailored based on specific needs:
-
Storage Areas: Optimized for easy access and organization of inventory.
-
Production Areas: Designed with specialized equipment or assembly lines in mind.
-
Loading/Unloading Docks: Positioned for easy flow of goods in and out of the warehouse.
6. Maintenance and Safety of Steel Structure Warehouses
Daily Maintenance
Steel structure warehouses require less maintenance than traditional buildings, but routine upkeep is still necessary:
Corrosion Control: Applying protective coatings and paints prevents rust.
Structural Inspections: Regularly inspecting joints, bolts, and beams ensures the warehouse remains safe and structurally sound.
Safety Features
Steel warehouses are designed with several safety features:
Earthquake Resistance: Many steel structures are built to withstand seismic activity, especially in regions prone to earthquakes.
Fire Resistance: Steel’s fire-resistant nature reduces the risk of fire-related damage.
7. Types of Steel Structure Warehouses
|
Type
|
Description
|
Typical Application
|
|
Single-Story Warehouse
|
Large-span, high-bay structure
|
Manufacturing, bulk storage
|
|
Multi-Story Warehouse
|
Vertical stacking, reinforced floors
|
Urban logistics, limited land areas
|
|
Heavy-Duty Warehouse
|
Reinforced columns/beams for machinery
|
Industrial equipment, production bases
|
|
Cold Storage Warehouse
|
Insulated panels, temperature control
|
Food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals
|
|
Logistics Distribution Center
|
Modular design with multiple loading bays
|
E-commerce, freight consolidation
|
Each type can be customized with mezzanines, skylights, overhead cranes, and insulated cladding to suit operational needs.
8. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Steel Warehouse
-
Site Conditions: Soil bearing capacity, wind exposure, and seismic zone classification.
-
Functional Requirements: Storage height, loading dock capacity, and equipment layout.
-
Budget and Lifecycle Cost: Consider not just initial cost, but energy use and maintenance.
-
Future Expansion: Modular and bolt-connected steel structures make future extensions easier.
-
Local Standards Compliance: Ensure the design meets ISO, ASTM, or local building codes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Steel Structure Warehouse
Choosing the right steel structure warehouse depends on your specific needs. Whether you're looking for a large-span single-story warehouse for manufacturing, a cold storage warehouse for sensitive products, or a multi-story warehouse for maximizing limited space, steel structures offer a wide range of options to suit every industry.
By considering factors like budget, space requirements, and future scalability, you can make an informed decision that meets your operational needs and supports your business growth.
If you’re still at the early planning stage and don’t yet have engineering drawings, don’t worry. We’ve prepared a practical guide explaining how to start a steel warehouse or factory project with only basic project information.
Read our detailed guide:
How to Buy a Steel Structure Warehouse Without Engineering Drawings



